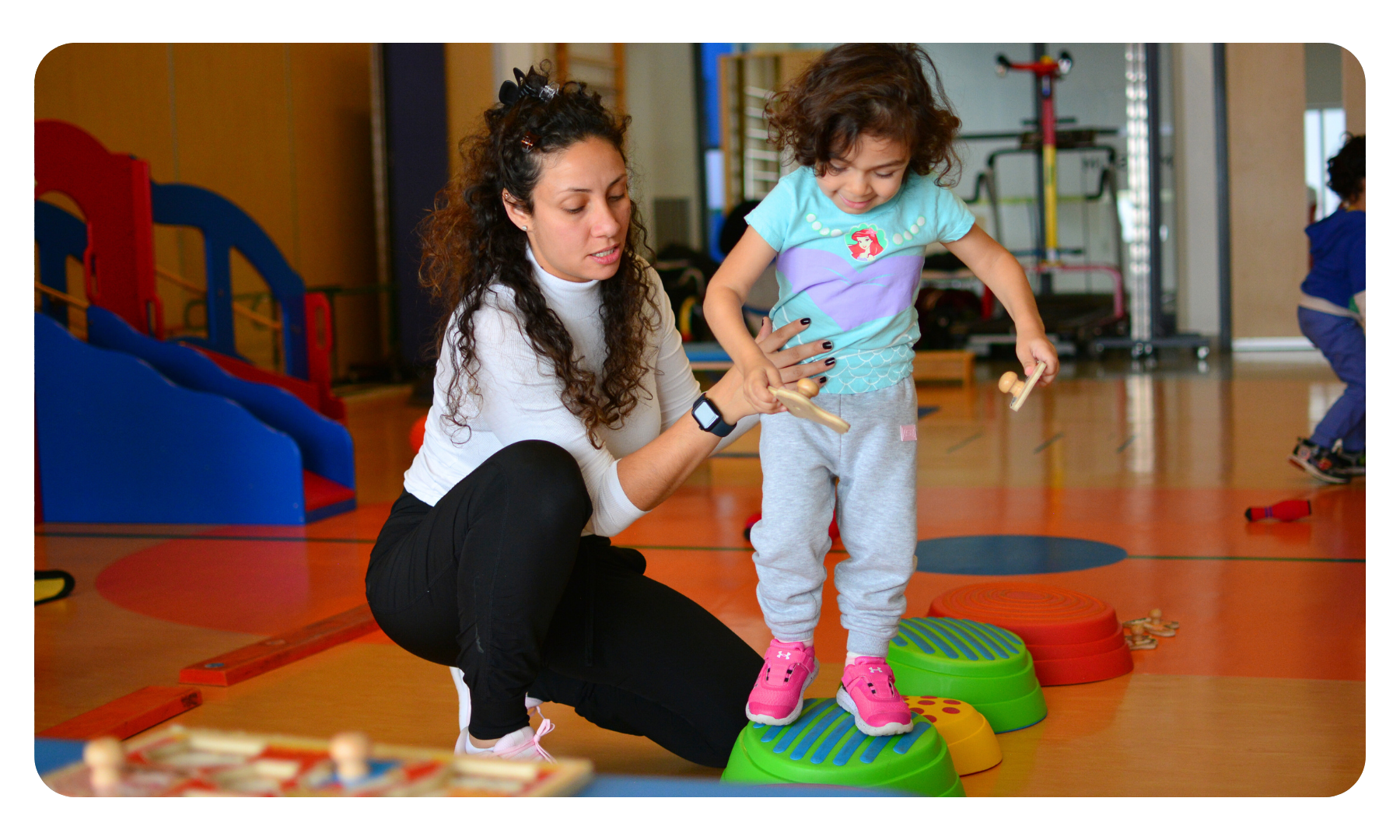
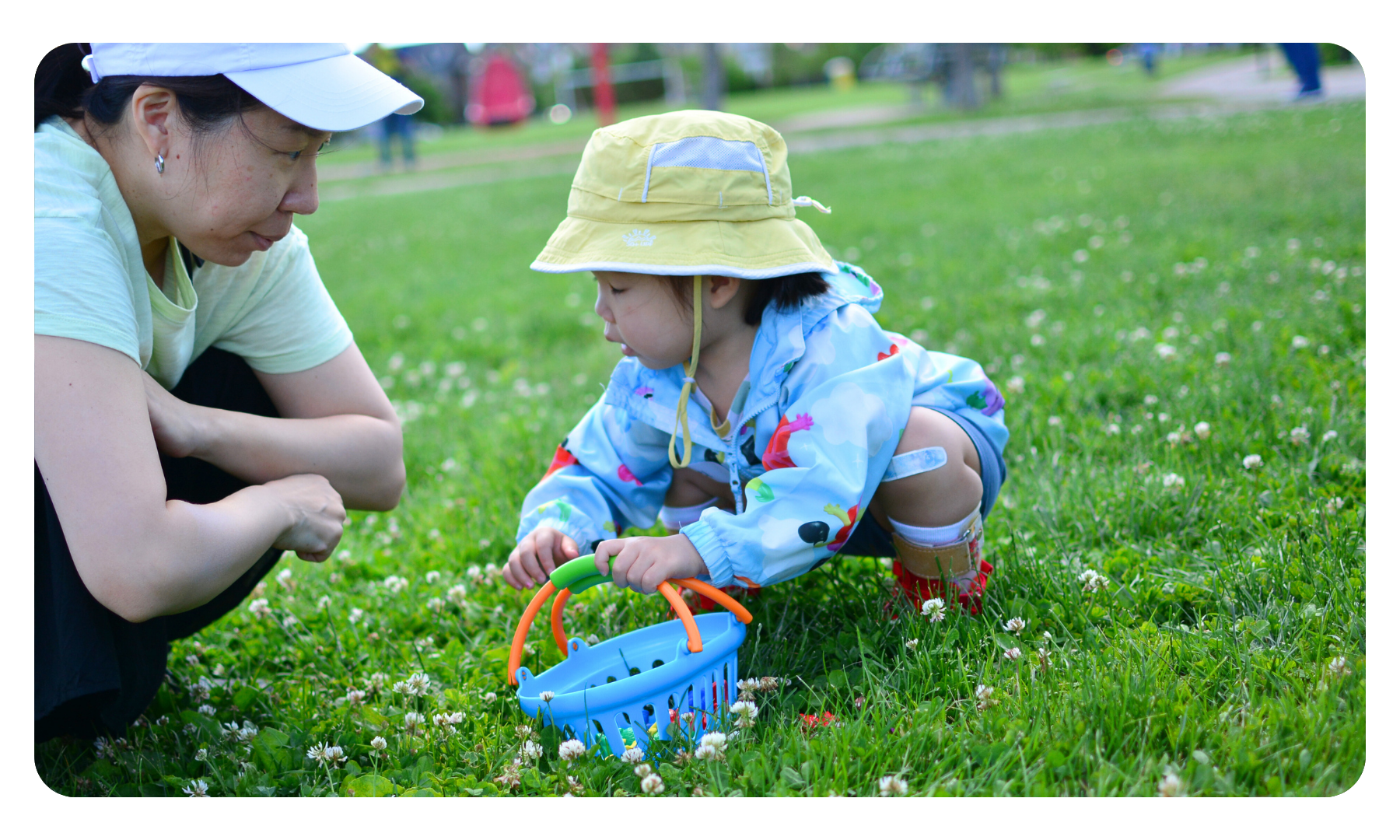
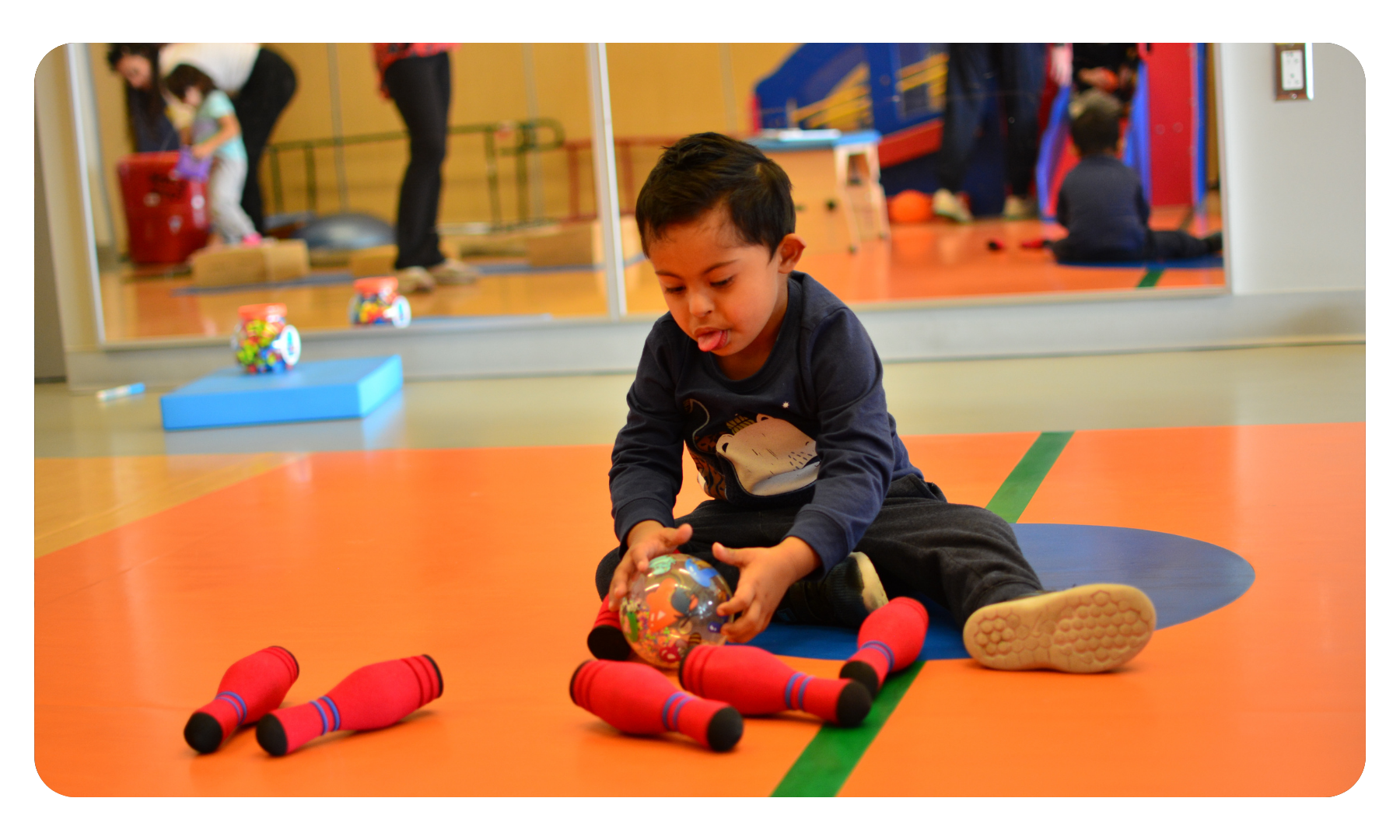
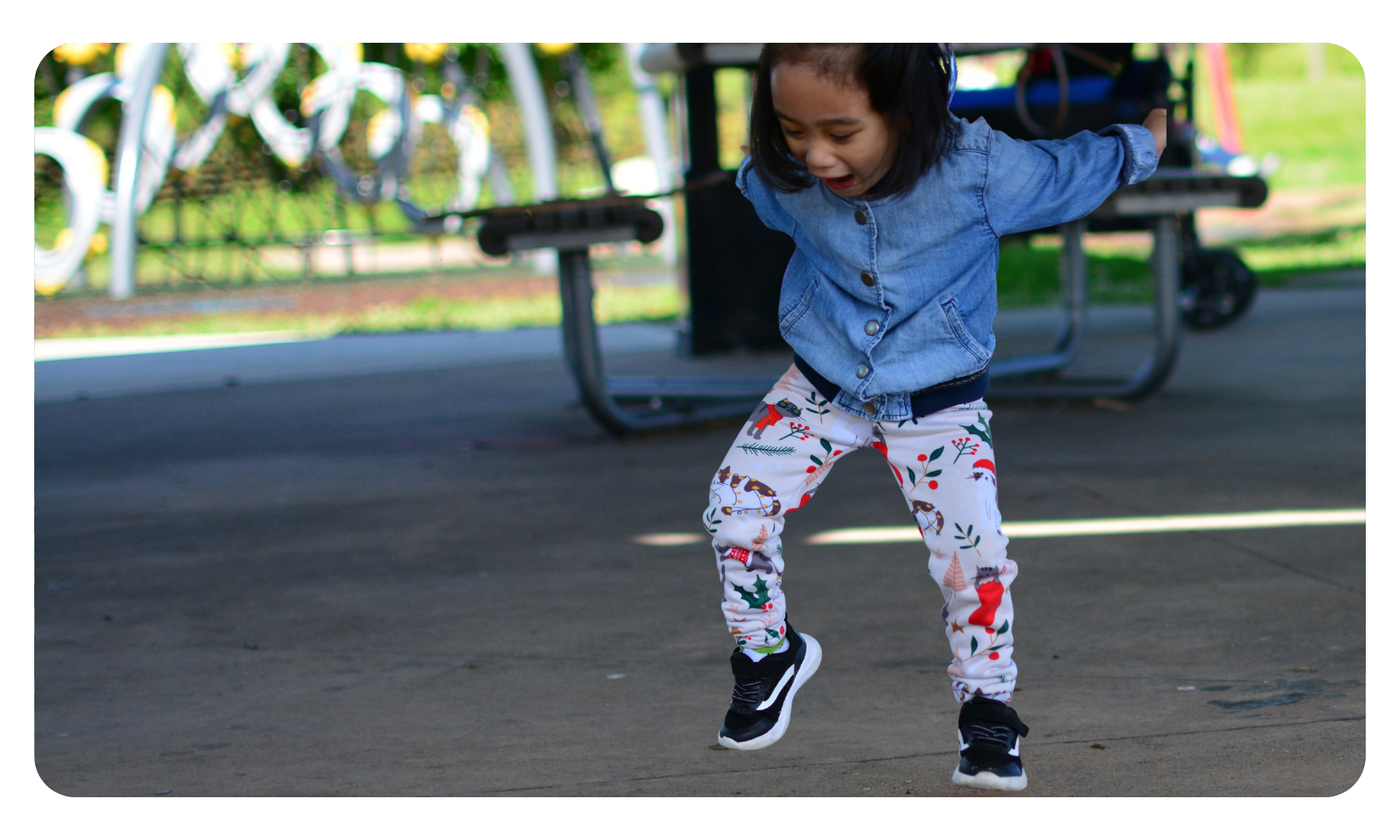
Gross Motor Skills
Gross motor skills are the ability to make movements using the large muscles in our body, including our arms, legs and torso (core). We use gross motor skills to perform activities such as standing, walking, running, jumping, throwing, kicking, etc. to support function and participation at home, school, work, and within everyday life.
External Resources
Explore our curated list of external resources that can help guide you through various areas of concern.
Intoeing
Pediatric intoeing, often called "pigeon toed," is when a child's feet turn inward while walking and/or running. This is a relatively common condition in young children and can be caused by various factors, including the position of the feet, legs, and/or hips.
What you Need to Know: Intoeing (CHEO)
Joint Hypermobility
Pediatric joint hypermobility is a condition where a child's joints move beyond the typical range of motion. This flexibility can sometimes lead to joint pain, more frequent injuries and potential difficulty with certain physical activities. Some children may benefit from general exercises to strengthen their muscles and support their joints.
Joint Hypermobility (CHEO)
Encouraging Time Outdoors
Encouraging children to spend more time outside can improve their physical health, boost their mood and enhance their creativity.
Helping your Child Spend More Time Outdoors (CHEO)
Tummy Time
Infant tummy time is a wonderful way to support your baby's growth. By placing baby on their tummy while they are awake and supervised, you help them build strong neck, shoulder, and arm muscles. These muscles are important for gross motor skills like rolling over, sitting up, and crawling. Tummy time also encourages development of these skills and helps prevent flat spots on their head.
Tummy Time: An Important Part of a Baby's Routine (TVCC)
Tummy Time: Activities to Strengthen Baby (Pathways)
W-Sitting
"W-sitting" is when children sit on the floor with their legs bent out to the sides in the shape of a "W." While generally not concerning, this position when sustained can put extra stress on a child’s hips, knees, and ankles, potentially affecting their posture and muscle development over time.
W-Sitting (TVCC)
Idiopathic Toe Walking
Idiopathic toe walking is when children walk on their toes without any known underlying reason beyond the age of 3 years old. While many children do outgrow this habit naturally, persistent toe walking can sometimes affect ankle range of motion, foot development and balance and muscle development.
Foot and Ankle: Idiopathic Toe Walking (SickKids)
These resources are provided for informational purposes only and are not a substitute for professional advice, diagnosis or treatment, provided by a qualified health-care provider. ErinoakKids is not responsible for the content, privacy policies and terms of use of any external websites we link.